

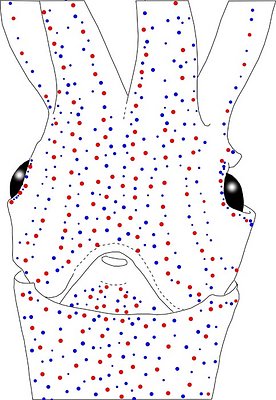
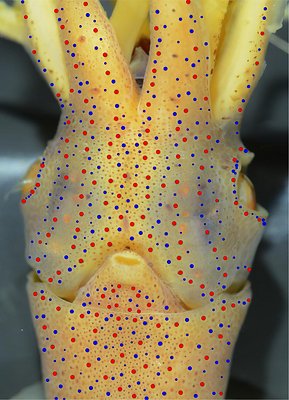
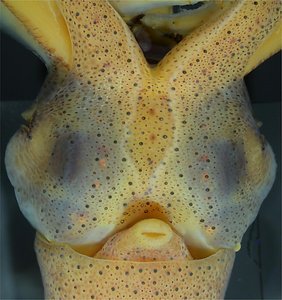
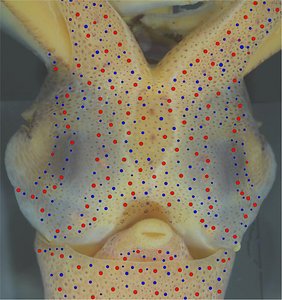
Figure. Ventral views of the head of Abraliopsis sp. B. Left - Photograph of the preserved squid showing photophores. Middle - Drawing from photograph of the same squid with two types of photophores. Right - Same squid with colored dots superimposed on the photograph to show the arrangement of two types of photophores. Red dots - Complex photophores (photophores with red color filters). Blue dots - Non-complex photophores (simple and lens bearing photophores). Photographs by R. Young

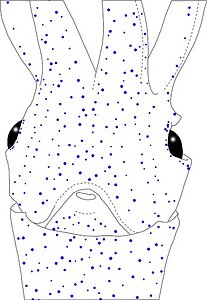
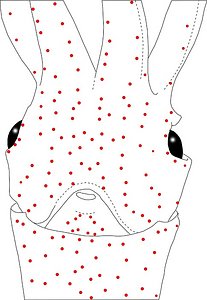
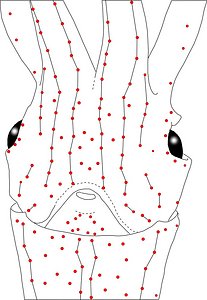
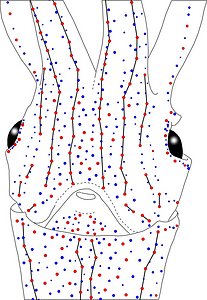
Figure. Same squid, same view as above. Left - Drawing showing only the non-complex (blue) photophores. Left middle - Drawing showing only the complex (red) photophores. Right middle - Same as previous drawing with lines connecting red photophores to aid comparisons of photophore patterns between species. Right - Drawing showing all photophores and lines showing red photophore patterns. Images by R. Young.

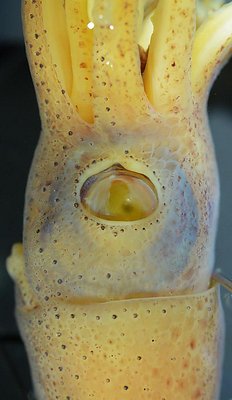
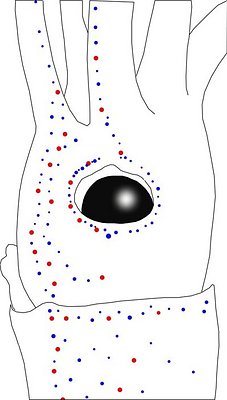
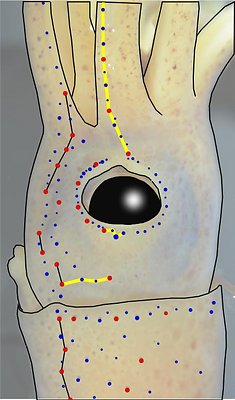
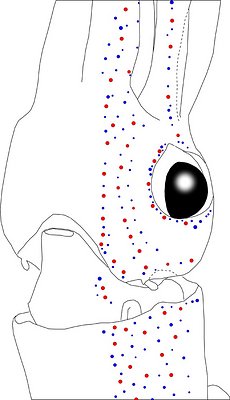
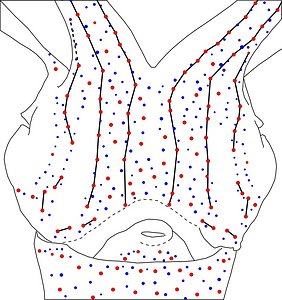
Figure. Side view of the head and proximal regions of the arms of the same squid (20 mm ML) as above. Left - Photograph of the preserved squid. Middle - Outline drawing from photograph with all integumental photophores represented by colored dots. Right - Outline drawing over dimmed photograph with all integumental photophores represented by colored dots, and with lines connecting some photophores. Red dots - Complex photophores. Blue dots - Non-complex photophores. Lines connecting photophores assist in understanding the organization of the photophores. Black lines - Patterns based on red photophores. Yellow line - Pattern based on red and blue photophores. Images by R. Young.
22 mm ML, mature male, New Caledonia waters

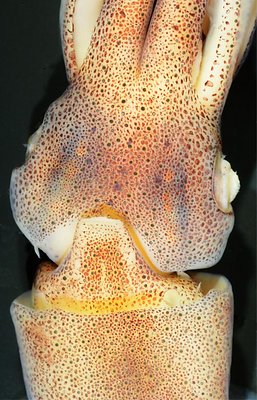
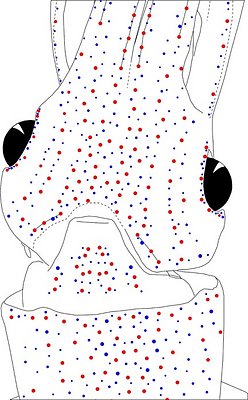
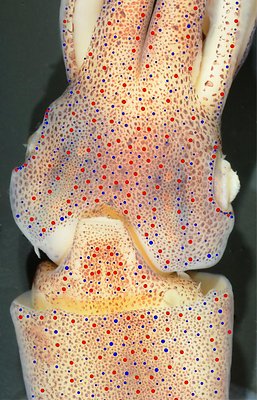
Figure. Ventral views of the head of Abraliopsis sp. B. Left - Photograph of the preserved squid showing photophores. Middle - Drawing from photograph of the same squid with two types of photophores. Right - Same squid with colored dots superimposed on the photograph to show the arrangement of two types of photophores. Red dots - Complex photophores (photophores with red color filters). Blue dots - Non-complex photophores (simple and lens bearing photophores). Photographs by R. Young

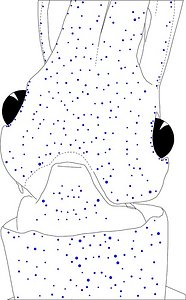
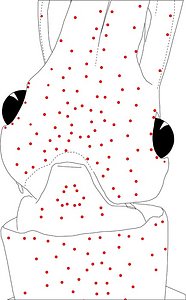
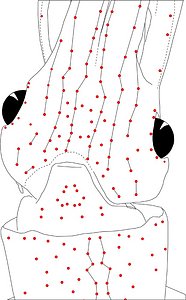
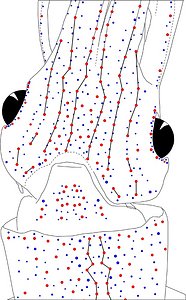
Figure. Same squid (22 mm ML, New Caledonia), same view as above. Left - Drawing showing only the non-complex (blue) photophores. Left middle - Drawing showing only the complex (red) photophores. Right middle - Same as previous drawing with lines connecting red photophores to aid comparisons of photophore patterns between species. Right - Drawing showing all photophores and lines showing red photophore patterns. Images by R. Young.

sp.nc3m22obliquepictsm.400a.jpg)
sp.nc3m22obliqpictrbpattsm1.400a.jpg)
Figure. Ventrolateral view of the head and proximal regions of the arms of the same squid (22 mm ML) as above. Left - Photograph of the preserved squid. Middle - Outline drawing from photograph with all integumental photophores represented by colored dots. Right - Outline drawing over dimmed photograph with all integumental photophores represented by colored dots, and with lines connecting some photophores. Red dots - Complex photophores. Blue dots - Non-complex photophores. Lines connecting photophores assist in understanding the organization of the photophores. Black lines - Patterns based on red photophores. Yellow line - Pattern based on red and blue photophores. Images by R. Young.
26 mm ML, mature female, Hawaiian waters
In this squid the photophore arrangements are very similar to the smaller male, only more photophores have been added with growth and some of the "blue" photophores have become "red" photophores
Figure. Ventral views of the head of Abraliopsis sp. B. Left - Photograph of the preserved squid showing photophores. Middle - Drawing from photograph of the same squid with two types of photophores. Right - Same squid with colored dots superimposed on the photograph to show the arrangement of two types of photophores. Red dots - Complex photophores (photophores with red color filters). Blue dots - Non-complex photophores (simple and lens bearing photophores). Photographs by R. Young

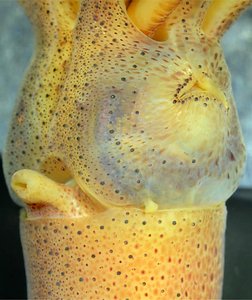
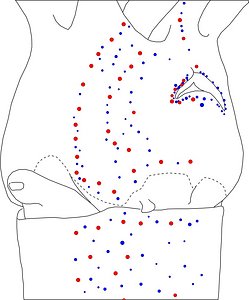
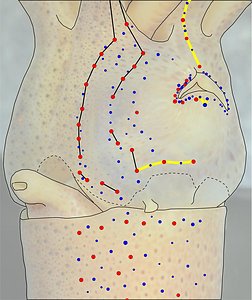
Figure. Ventrolateral view of the head and proximal regions of the arms of the same squid (26 mm ML) as above. Left - Photograph of the preserved squid. Middle - Outline drawing from photograph with all integumental photophores represented by colored dots. Right - Outline drawing over dimmed photograph with all integumental photophores represented by colored dots, and with lines connecting some photophores. Red dots - Complex photophores. Blue dots - Non-complex photophores. Lines connecting photophores assist in understanding the organization of the photophores. Black lines - Patterns based on red photophores. Yellow line - Pattern based on red and blue photophores. Images by R. Young.

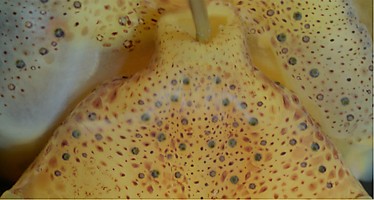
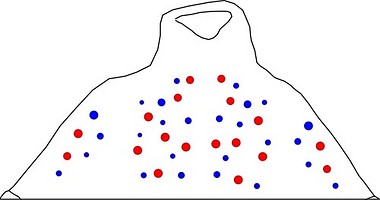
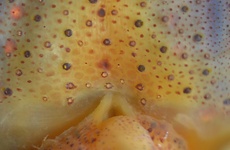
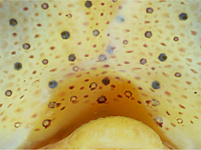
Figure. Ventral view of the funnel of the same squid (26 mm ML). Left - Photograph of the funnel showing the integumental photophores. Right - Drawing of the funnel with colored dots showing the positions of the integumental photophores.
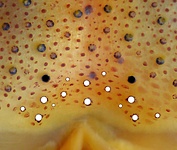
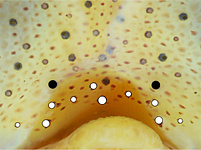
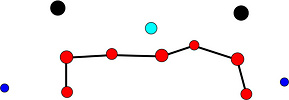
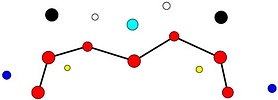
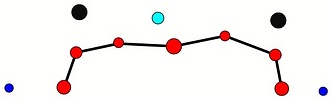
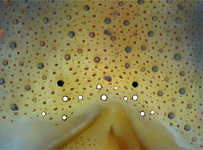
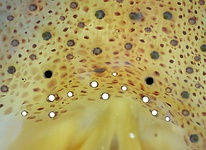
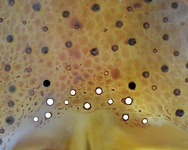
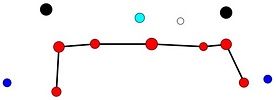
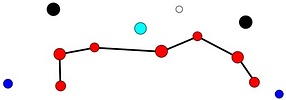
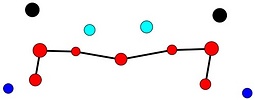
Tables. Ventral views of the funnel-groove region of Abraliopsis sp. B. Top tier - Photograph of the preserved squid showing photophores of the funnel groove and surrounding tissue. Middle tier - In the photograph, white dots are placed over the "white" photophores of the funnel groove. Black dots are placed over the two most posteromedial "red" photophores of the ventral head to mark the anterolateral edges of the funnel groove. Bottom tier - Same pattern of dots as in photographs but dots are colored. Colored dots, lines - Aid in comparison of patterns between species. Open dots - Represent photophores that are either of uncertain status as "white" photophores or have variable presence. Images by R. Young. Comparison of white photophore patterns for all Abraliopsis species can be found here.
| Mature male, 19 mm ML | Mature female, 24 mm ML | Mature female, 26 mm ML. Preserved |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
| Mature female, 27 mm ML | Mature female, 27 mm ML | Mature female, 29 mm ML |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
Comments: Summary of photophore distributions.(photophore definitions found here)
ARMS:
Medial Arm IV Series - Continuous; reaches about 3/4 of arm length.
Central Arm IV Sector - Scattered blue photophores present near arm base.
Lateral Arm IV Series - Reaches arm tip; continuous.
Lateral Membrane Series of arm IV - Reaches about 1/2 to 2/3 of arm length; continuous.
Arm III Series - Nearly reaches arm tip (>85% of arm length).
HEAD - Typical scattered pattern with:
Median Head Series - Absent.
Median Head Sector - Scattered photophores; about 7 red photophores at 20 mm ML, about 9 red photophores at 26 mm ML.
Medial Head Series - Arbitrary designation: About 6-8 red photophores.
Lateral Head Sector - Scattered photophores; at 20 mm ML about 2 red photophores, about 6 at 26 mm ML.
Lateral Head Series - Fairly well defined.
Window Sector - Few scattered blues at either end. Otherwise without photophores.
1st Lateral Window Series - Two postertior segments containing 2 red photophores each; one anterior segment containing 5 red photophores at 20 mm ML and 6 at 26 mm ML.
2nd Lateral Window Series - Not present; 1-3 red photophores (1 at 20, 27 mm, 2 at 22, 26, 27 mm and 3 at 29 mm ML).
Eyelid Series - Red photophores only on ventral half of eyelid. Posterior Eyelid Series with one large blue photophores displaced slightly posteriorly from eyelid series. Formula: RbBB at 20, 22, 26, 27 mm ML and RbbBB at 29 mm ML.
Occipital Series - RbbR at 20 mm ML; RbRbR at 22 and 26 mm ML; RbRbR at 26 mm ML.
Lateral Funnel-groove Series - Three or four red photophores in two segments (2+1 or 2+2) at 20 mm ML, four in two segments at 26 mm ML; poorly aligned segments.
Olfactory Photophore - Red at 27 mm ML.
White Patch (funnel groove) - Moderate Pattern (red, blue, cyan; plus occasionally yellow).
FUNNEL: Patches not well demarcated.
Medial Patch - Scattered red photophores.
Lateral Patch - Two red photophores.
MANTLE - Typical scattered pattern with:
Median Mantle Sector - Narrow. Median bare strip present but not readily apparent anteriorly.
Medial Mantle Series - Irregular.
Mediolateral Mantle Sector - Scattered photophores; Lateral Mantle Series not apparent..
Mantle-angle series - Barely recognizable.



 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site