Mollusca
Snails, clams, mussels, squids, octopi, chitons, and tusk shells


This tree diagram shows the relationships between several groups of organisms.
The root of the current tree connects the organisms featured in this tree to their containing group and the rest of the Tree of Life. The basal branching point in the tree represents the ancestor of the other groups in the tree. This ancestor diversified over time into several descendent subgroups, which are represented as internal nodes and terminal taxa to the right.

You can click on the root to travel down the Tree of Life all the way to the root of all Life, and you can click on the names of descendent subgroups to travel up the Tree of Life all the way to individual species.
For more information on ToL tree formatting, please see Interpreting the Tree or Classification. To learn more about phylogenetic trees, please visit our Phylogenetic Biology pages.
close boxReferences
Beesley, P. L., G. J. B. Ross, and A. Wells (eds.) 1998. Mollusca: The Southern Synthesis. Fauna of Australia, Vol 5. Part A and B. CSIRO Publishing, Melbourne.
Haszprunar, G. 2000. Is the Aplacophora monophyletic? A cladisitic point of view. American Malacological Bulletin 15:115-130.
Medina, M. and A. G. Collins. 2003. The role of molecules in understanding molluscan evolution. Pages 14-44 in: Molecular Systematics and Phylogeography of Mollusks. C. Lydeard and D. R. Lindberg, eds. Smithsonian Institution, Washington, DC.
Passamaneck, Y. J., C. Schander, and K. M. Halanycha. 2004. Investigation of molluscan phylogeny using large-subunit and small-subunit nuclear rRNA sequences. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 32(1):25-38.
Rosenberg, G. 1992. The Encyclopedia of Seashells. The Five Mile Press, New York.
Runnegar, B. and J. J. Pojeta. 1985. Origin and diversification of the Mollusca. Pages 1-57 in The Mollusca, E. R. Trueman and M. R. Clarke, eds. Academic Press, New York.
Sigwart, J. D. and M. D. Sutton. 2007. Deep molluscan phylogeny: synthesis of palaeontological and neontological data. Proceedings of the Royal Society Series B 274(1624):2413-2419.
Steiner, G. and H.Dreyer. 2003. Molecular phylogeny of Scaphopoda (Mollusca) inferred from 18S rDNA sequences: support for a Scaphopoda-Cephalopoda clade. Zoologica Scripta 32(4):343-356.
Taylor, J. D., ed. 1996. Origin and Evolutionary Radiation of the Mollusca. Centenary Symposium of the Malacological Society of London. Oxford University Press, Oxford. 392 pp.
Vermeij, G. J. 1993. A Natural History of Shells. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ.
Information on the Internet
- Mollia Homepage - Mollusca Information. University of California Museum of Paleontology.
- Selected Sources of Information on Mollusks. Smithsonian Institution.
- Mollusc Specialist Group. International Union for the Conservation of Nature, Species Survival Commission.
- Freshwater Mollusk Conservation Society.
- Systematic Research Collections: Mollusca.
- Conchologists of America -- Conch-Net HomePage.
- American Malacological Society (Union).
- Malakos. Un lugar para los amantes de los Moluscos y coleccionistas de conchas.
- Man and Mollusc. Resource site for students, educators, and anyone wanting to learn more about the fascinating world of the molluscs.
Title Illustrations

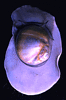
| Scientific Name | Lunatia |
|---|---|
| Acknowledgements | Gray Museum Slide Collection |
| Copyright |
© 1995 Marine Biological Laboratory, Woods Hole
|
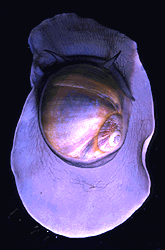
| Scientific Name | Placopecten magellanicus (top), Polyplacophora (bottom) |
|---|---|
| Acknowledgements | Gray Museum Slide Collection |
| Copyright |
© Marine Biological Laboratory, Woods Hole

|
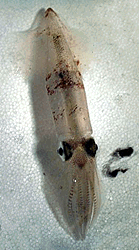
| Scientific Name | Loligo pealei |
|---|---|
| Creator | Photograph by David Remsen |
| Acknowledgements | Gray Museum Slide Collection |
| Copyright |
© 1995 Marine Biological Laboratory, Woods Hole

|
About This Page
Page copyright © 1995
All Rights Reserved.
Citing this page:
Tree of Life Web Project. 1995. Mollusca. Snails, clams, mussels, squids, octopi, chitons, and tusk shells. Version 01 January 1995 (temporary). http://tolweb.org/Mollusca/2488/1995.01.01 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/







 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site