Abraliopsis affinis
Lourdes Burgess, Richard E. Young, and Kotaro TsuchiyaIntroduction
A. affinis is one of the more easily recognized members of the subgenus. Males reach a length of at least 35 mm ML and females a length of 43 mm ML. This species is restricted in its distribution to the Eastern Tropical Pacific.
Brief diagnosis:
An Abraliopsis (Pfefferiteuthis) with ...
- key-hole shaped, bare region (lacks photophores) on anteroventral mantle.
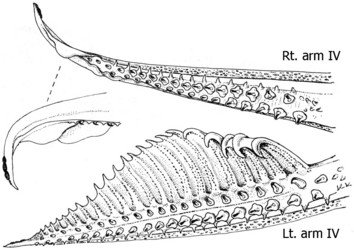
- long gaps separate photophore patches on Lateral Arm IV Series and Arm III Series.
- 3 red photophores in caret at posterior end of Median Head Series.
Characteristics
In addition to familial characters (listed on the Enoploteuthidae page) and generic characters (listed on the Abraliopsis page), Abraliopsis affinis has:
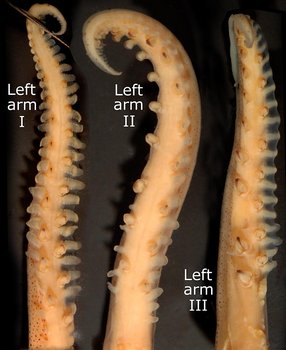
- Arms
- Arms IV about 75% of ML.
- Arms I-III with 15 - 30 hooks and distal suckers.
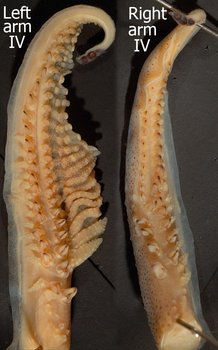
- Female with ca.25 hooks on arm IV; male with ca. 30 hooks on hectocotylized arm (right arm IV) and ca. 40 hooks on modified left arm IV.
- Hectocotylus (right arm IV) with two subequal-sized offset flaps.
- Protective membrane and with elongate spatulate trabeculae very large on left arm IV, and with small, conical tubercules on trabeculae.
- Oral base of arms I-III with conical tubercules.
- Trabeculae of arms I well developed in protective membranes on both margins; small tubercules along oral margins of trabeculae.
- Arms II & III with much larger trabeculae in membranes of ventral than dorsal margins; tubercules absent from trabeculae.
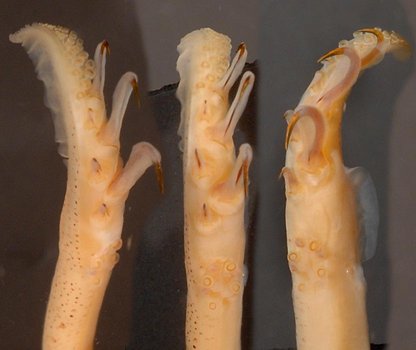
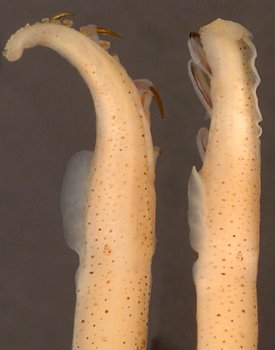
- Arms III in males with proximal 5 or more suckers on dorsal margin much larger than counterparts on ventral margin. Proximal sucker of the ventral series small and equal in size to next ventral hook (see photograph below).
- Largest suckers of distal arm with about 6 truncated teeth on distal margin; arms I with most suckers (~26) and arms III the least (~9). LB
- Tentacle clubs
- Manus with large ventral hooks about 2.5 times height of dorsal counterparts..
- Carpal flap and aboral keel, large.
- Three or four hooks in each series.
- Photophores
- Ocular photophores: 5 photophores with terminal photophores about 2X diameter of adjacent ones.
- Integumental photophores: 3 series on venral head; 6 poorly defined series on mantle with some scattered red photophores.
 Click on an image to view larger version & data in a new window
Click on an image to view larger version & data in a new window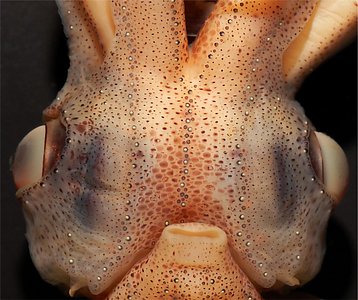
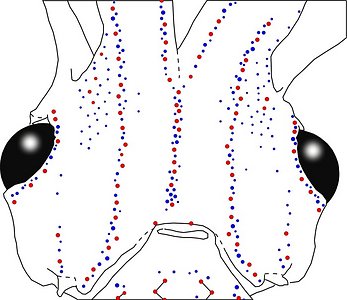
Figure. Ventral views of the integumental photophores of A. affinis, mature male, 33 mm ML. Left - Photograph of preserved squid. Right - Outline drawing from photograph with all integumental photophores represented by colored dots. Red dots - Complex photophores. Blue dots - Non-complex photophores. Images by R. Young.
Detailed information on the integumental photophores can be found here.
- Ocular photophores: 5 photophores with terminal photophores about 2X diameter of adjacent ones.
- Viscera
- Spermatangia receptacles - Females with three pockets for storing spermatangia: A Stellate Pocket at the junction of the anterior end of the gladius and the visceral mass, and between the stellate ganglia; two Dorsal-collar Pockets on the inner surface of the collar at its anterodorsal end.
- Spermatangia receptacles - Females with three pockets for storing spermatangia: A Stellate Pocket at the junction of the anterior end of the gladius and the visceral mass, and between the stellate ganglia; two Dorsal-collar Pockets on the inner surface of the collar at its anterodorsal end.
Comments
Comparisons of all species in the subgenus can be found on the Abraliopsis (Pfefferiteuthis) page.
Distribution
Geographical Distribution
This species is distributed in the tropical East Pacific between 20° N and 20° S (Okutani, 1974; Alexeyev, 1995), westward at least to 126° W (Nesis, 1982/87).
References
Alexeyev, D.O. 1994. New data on the distribution and biology of squids from the southern Pacific. Rutenica, 4:151-166.
Nesis, K. N. 1982. Abridged key to the cephalopod mollusks of the world's ocean. 385+ii pp. Light and Food Industry Publishing House, Moscow. (In Russian.). Translated into English by B. S. Levitov, ed. by L. A. Burgess (1987), Cephalopods of the world. T. F. H. Publications, Neptune City, NJ, 351pp.
Okutani, T. 1974. Epipelagic decapod cephalopods collected by midwater tows during the EASTROPAC Expedition, 1967-1968 (systematic part). Bull. Tokai Reg. Fish. Res. Lab., 80:29-118.
Title Illustrations

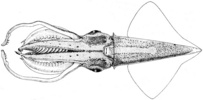
| Scientific Name | Abraliopsis affinis |
|---|---|
| Location | tropical East Pacific |
| Reference | Okutani, T. 1974. Epipelagic decapod cephalopods collected by midwater tows during the EASTROPAC Expedition, 1967-1968 (systematic part). Bull. Tokai Reg. Fish. Res. Lab., 80:29-118. |
| Sex | Male |
| Copyright | © 1974 T. Okutani |
| Scientific Name | Abraliopsis affinis |
|---|---|
| Location | Eastern tropical Pacific at 8°36'N, 81°14'W |
| Specimen Condition | Preserved |
| Sex | Male |
| Life Cycle Stage | Mature |
| View | Ventral |
| Size | 29 mm ML |
| Collection | SBMNH 49499 |
| Image Use |
 This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0. This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0.
|
| Copyright |
©
Richard E. Young

|
About This Page
Lourdes Burgess

Retired
Richard E. Young

University of Hawaii, Honolulu, HI, USA
Kotaro Tsuchiya

Tokyo University of Fisheries, Tokyo, Japan
Page copyright © 2013 Lourdes Burgess , Richard E. Young , and Kotaro Tsuchiya
 Page: Tree of Life
Abraliopsis affinis .
Authored by
Lourdes Burgess, Richard E. Young, and Kotaro Tsuchiya.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
Page: Tree of Life
Abraliopsis affinis .
Authored by
Lourdes Burgess, Richard E. Young, and Kotaro Tsuchiya.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
- Content changed 03 November 2013
Citing this page:
Burgess, Lourdes, Richard E. Young, and Kotaro Tsuchiya. 2013. Abraliopsis affinis . Version 03 November 2013 (under construction). http://tolweb.org/Abraliopsis_affinis/19682/2013.11.03 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/








 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site