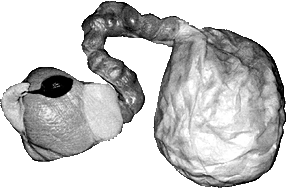
- Arms and web
- Arm formula 1>2>3>4 or 2>1>3>4; longest arm 65-78% of TL, shortest arm 46-71% of ML.
- Sexual dimorphism in suckers absent.
- Sucker numbers 3-4 small, next 30-35 suckers of similar size but slightly enlarged, next 30-35 suckers (those beyond web margin) rapidly decrease in size to arm tip.
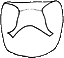
- Suckers with small suction chamber, large, simple sucker aperature (drawing on right).
- Arm sucker counts to 88; more numerous in females than males of similar size.
- Web nodules absent.
- Cirri short, 3-6% of ML or 0.7-1.2 times largest sucker diameter.
- First cirri between suckers 1 and 2.
- Web sectors A and B deepest, E shallowest.
- Eyes
- Eyes large.
- Eyes large.
- Funnel
- Form of funnel organ unknown.
- Form of funnel organ unknown.
- Fins
- Fins massive; length 85-173% of ML; width 36-43% of fin length.
- Fins massive; length 85-173% of ML; width 36-43% of fin length.
- Mantle cavity
- Mantle septum with thin adductor muscle anteriorly and thin membrane posteriorly.
- Gills half-orange shape.
- Gills with 7-8 primary lamellae (inner- and outer-most reduced in size).
- Optic lobe and nerves
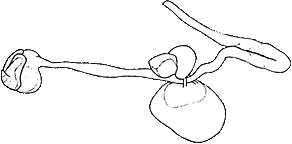
- Optic lobe kidney-shaped.
- 7-8 optic nerve bundles pass through/by white body.
- White bodies (violet colored) fused in dorsal midline.
 Click on an image to view larger version & data in a new window
Click on an image to view larger version & data in a new window
Figure. Optic lobe, optic nerve bundles and white body of C. hochbergi, male, 86 mm ML. Drawing from O'Shea (1999).
- Digestive tract
- Radula absent.
- Salivary glands absent.
- Crop absent.
- Stomach and caecum about equal in size.
- Intestine about 2.5 times esophagus in length.
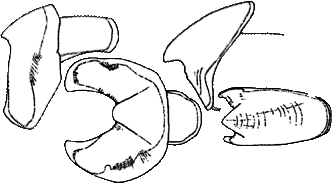
- Beaks
- Upper beak (right) with square crest; jaw minutely serrate (2 or 3 teeth); rostrum sharp, slightly deflected down; weak lateral-wall fold.
- Lower beak (left) rostrum with blunt tip. Photographs of the beaks can be found here.
- Male reproductive system
- Terminal accessory gland largest.
- Penis small, flimsy, triangular, lappet-like.
- Female reproductive system
- Proximal oviduct about 5 times length of distal oviduct.
- Oviducal gland massive; distal portion nearly twice length of proximal portion.
- Pigmentation
- One white patch at the base of each fin and below each eye.
- Dorsal surfaces mauve to purple.
- Ventral surface of mantle and dorsal and ventral surfaces of fins slightly paler, reddish.
- Edges of eyelids white to pale mauve.
- Oral surfaces of web sectors A, B and C (to sucker 16-18) and D and E (to sucker 12-13) deep mauve to purple; outer oral surfaces of web and oral surfaces of arms and suckers white to pale mauve.
- Measurements and counts
Measurements are from O'Shea (1999). Measurements from right and left sides are averaged and rounded.Sex Female Male? Male Male ? ML, mm 151 126 89 88 58 MW, mm 132 105 132 91 57 Fin length 158 108 154 81 78 Fin width 47 47 64 32 29 Length, arm I 324 274 290 170 145 Length, arm II 316 279 325 170 148 Length, arm III 314 271 304 162 154 Length, arm IV 300 255 280 147 140 Web depth, sect. A 194 150 120 117 90 Web depth, sect. B 174 160 162 117 87 Web depth, sect. C 157 142 163 95 82 Web depth, sect. D 131 123 100 80 70 Web depth, sect. E 81 67 78 50 48 Sucker counts, arm I 86 78 72 72 77 Sucker counts, arm II 88 77 77 74 77 Sucker counts, arm III 86 78 72 72 73 Sucker counts, arm IV 84 79 73 70 74 Max. arm sucker diam. 5.5-6.0 5.2-6.0 6.0-7.0 3.0-3.1 2.5-3.0 Number, gill lamellae 7 7 7 7 8
Cirroctopus hochbergi Description Continued
Steve O'Shea, Richard E. Young, and Michael VecchioneReferences
O'Shea, Steve. 1999. The Marine Fauna of New Zealand: Octopoda (Mollusca: Cephalopoda). NIWA Biodiversity Memoir 112: 280pp.
About This Page
Steve O'Shea

Oceanic Sciences Research Institute, Auckland University of Technology, Auckland, New Zealand
Richard E. Young

University of Hawaii, Honolulu, HI, USA
Michael Vecchione

National Museum of Natural History, Washington, D. C. , USA
Page copyright © 2002 Steve O'Shea , Richard E. Young , and Michael Vecchione
All Rights Reserved.


 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site