Staphylinoidea


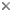
This tree diagram shows the relationships between several groups of organisms.
The root of the current tree connects the organisms featured in this tree to their containing group and the rest of the Tree of Life. The basal branching point in the tree represents the ancestor of the other groups in the tree. This ancestor diversified over time into several descendent subgroups, which are represented as internal nodes and terminal taxa to the right.

You can click on the root to travel down the Tree of Life all the way to the root of all Life, and you can click on the names of descendent subgroups to travel up the Tree of Life all the way to individual species.
For more information on ToL tree formatting, please see Interpreting the Tree or Classification. To learn more about phylogenetic trees, please visit our Phylogenetic Biology pages.
close boxPhylogeny after Lawrence and Newton 1982, Caterino et al. 2005, and Beutel and Leschen 2005.
Unless otherwise stated, the generic classifcation used throughout the staphylinoids in the ToL follows Newton and Thayer (2005).
References
Betz, O., M. K. Thayer & A. F. Newton. 2003. Comparative morphology and evolutionary pathways of the mouthparts in spore-feeding Staphylinoidea (Coleoptera). Acta Zoologica 84 (3): 179-238.
Beutel, R. G. and Leschen, R. A. B. 2005. Phylogenetic analysis of Staphyliniformia (Coleoptera) based on characters of larvae and adults. Systematic Entomology DOI:10.1111/j.1365-3113.2005.00293.x
Caterino, M. S., T. Hunt, and A. P. Vogler. 2005. On the constitution and phylogeny of Staphyliniformia (Insecta:Coleoptera). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 34: 655 -672. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2004.11.012
Lawrence, J. F. and A. F. Newton. 1982. Evolution and classification of beetles. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 13: 261-290.
Newton, A. F., Jr. 1984. Mycophagy in Staphylinoidea (Coleoptera). Pages 302-353 in: Q. Wheeler and M. Blackwell (editors), Fungus/Insect Relationships. Perspectives in Ecology and Evolution. Columbia University Press, New York.
Newton, A. F., Jr. 1985. South temperate Staphylinoidea (Coleoptera): their potential for biogeographic analysis of austral disjunctions. Pages 180-220 in: G. E. Ball (editor), Taxonomy, phylogeny, and zoogeography of beetles and ants. A volume dedicated to the memory of Philip Jackson Darlington, Jr., 1904-1983. W. Junk, The Hague, Series Entomologia 33.
Newton, A. F., Jr. 1990. Larvae of Staphyliniformia (Coleoptera): where do we stand? Coleopterists Bulletin 44: 205-210.
Newton, A. F., Jr. & M. K. Thayer. 1992. Current classification and family-group names in Staphyliniformia (Coleoptera). Fieldiana: Zoology (N. S.) 67: 1-92.
Newton, A. F. & M. K. Thayer. 2005 Catalog of higher taxa, genera, and subgenera of Staphyliniformia. Chicago: Field Museum of Natural History. URL: http://www.fieldmuseum.org/peet_staph/db_1a.html
Information on the Internet
- PEET Austral Staphylinidae. Systematics and Historical Biogeography. The Field Museum
Title Illustrations

| Scientific Name | Agathidium |
|---|---|
| Specimen Condition | Dead Specimen |
| Image Use |
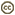 This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0. This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0.
|
| Copyright |
© 1995 David R. Maddison

|
| Scientific Name | Nanosella |
|---|---|
| Location | Chile |
| Comments | Fully winged specimen, wings removed |
| Acknowledgements | Specimen slide made by A. F. Newton |
| Specimen Condition | Dead Specimen |
| Identified By | A. F. Newton |
| Sex | Female |
| Life Cycle Stage | adult |
| Image Use |
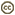 This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License - Version 3.0. This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License - Version 3.0.
|
| Copyright |
© 2003 Margaret K. Thayer

|
| Scientific Name | Nicrophorus quadrimaculatus Matthews, 1888 |
|---|---|
| Specimen Condition | Live Specimen |
| Sex | Female |
| Image Use |
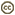 This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0. This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0.
|
| Copyright |
© 1995 David R. Maddison

|
| Scientific Name | Staphylinidae |
|---|---|
| Specimen Condition | Live Specimen |
| Image Use |
 This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0. This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0.
|
| Copyright |
© 1995 David R. Maddison

|
About This Page
Correspondence regarding this page should be directed to Margaret K. Thayer at
mthayer@fieldmuseum.org
Page copyright © 2006 Margaret K. Thayer
 Page: Tree of Life
Staphylinoidea .
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
Page: Tree of Life
Staphylinoidea .
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
- Content changed 19 November 2006
Citing this page:
Tree of Life Web Project. 2006. Staphylinoidea . Version 19 November 2006 (temporary). http://tolweb.org/Staphylinoidea/9076/2006.11.19 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/







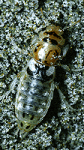




 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site