Rhipsideigma
Thomas Hörnschemeyer

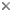
This tree diagram shows the relationships between several groups of organisms.
The root of the current tree connects the organisms featured in this tree to their containing group and the rest of the Tree of Life. The basal branching point in the tree represents the ancestor of the other groups in the tree. This ancestor diversified over time into several descendent subgroups, which are represented as internal nodes and terminal taxa to the right.

You can click on the root to travel down the Tree of Life all the way to the root of all Life, and you can click on the names of descendent subgroups to travel up the Tree of Life all the way to individual species.
For more information on ToL tree formatting, please see Interpreting the Tree or Classification. To learn more about phylogenetic trees, please visit our Phylogenetic Biology pages.
close boxIntroduction
Five extant species of Rhipsideigma are known: Four of them, R. lugubris (Fairmaire, 1895), R. raffrayi (Fairmaire, 1884), R. adjuncta Neboiss, 1984 and R. anosibense Neboiss, 1989, are endemics of Madagascar. The fifth species, R. cretaceotincta (Kolbe, 1897), occurs in Tanzania on the east coast of Africa, slighly north of Madagascar.
R. raffrayi is the only species of which a larva has been described and investigated (Beutel & Hörnschemeyer 2002). There is no information on the life-cycle, host plants or any other aspect of the biology of these species.

Rhipsideigma. © Thomas Hörnschemeyer
Characteristics
The species of Rhipsideigma are comparatively large cupedid beetles. The smallest, R. lugubris, reaches 13mm of length but all others are 15mm to 20mm long and up to 6 mm wide.
The coloration is composed of different shades of brown with lighter, in R. cretaceotincta white, areas on head and prothorax and at the tips of the elytra. R. lugubris is a conspicuous exception here, with a black body and bright orange markings on head and prothorax.
Characteristic of all species of Rhipsideigma are the large, erect head tubercles, which are distinctly more prominent in this genus than in most other Archostemata. Exceptions are Cupes capitatus and Tenomerga leucophaea where similarly large tubercles are present.



Rhipsideigma lugubris (left), Rhipsideigma raffrayi (right) © Thomas Hörnschemeyer
Discussion of Phylogenetic Relationships
According to Hörnschemeyer (2009) the closest relatives of Rhipsideigma are Cupes capitatus Fabricius, 1801 and Tenomerga leucophaea (Newman, 1839). Characters of the head, the mouthparts and especially the male genitalia indicate that the north American C. capitatus is the sistergroup of Rhipsideigma. The south African T. leucophaea then is the sistergroup to C. capitatus + Rhipsideigma.
References
Beutel, R. G. and T. Hörnschemeyer. 2002. Description of the larva of Rhipsideigma raffrayi (Coleoptera: Archostemata), with phylogenetic and functional implications. European Journal of Entomology 99:53-66.
Fabricius, J. C. 1801. Systema Eleutheratorum. Kiliae 2: 66-67.
Fairmaire, L. 1884. Note sur les Coléoptères receuillis par M. Ach. Raffray á Madagascar et descriptions des espéces nouvelles - 1re Partie. Annales de la Societe Entomologique de France 4: 223-242.
Fairmaire, L. 1895. Un Coléoptére nouveaux de Madagascar. Annales de la Societe Entomologique de France 64: clxxi - clxxii.
Hörnschemeyer, T. 2009. The species-level phylogeny of archostematan beetles - where do Micromalthus debilis and Crowsoniella relicta belong? Systematic Entomology 34(3): 533-558.
Kolbe, H. J. 1897. Afrikanische Coleoptera des Königlichen Museums für Naturkunde zu Berlin. Entomologische Nachrichten 23: 348-355.
Neboiss, A. 1984. Reclassification of Cupes Fabricius (s.lat.), with descriptions of new genera and species (Cupedidae: Coleoptera). Systematic Entomology 9:443-447.
Neboiss, A. 1989. New species of Archostemata (Coleoptera, Ommatidae, Cupedidae). Revue francaise Entomologie (N.S.) 11(3): 109-115.
Newman, E. 1839. XXXV.-Supplementary note to the synonymy of Passandra. Annals and Magazine of Natural History (Zoology, Botany, and Geology) 3(18): 303 - 305.
Title Illustrations

| Scientific Name | Rhipsideigma raffrayi (Cupedidae) |
|---|---|
| Image Use |
 This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0. This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0.
|
| Copyright |
© 1996 David R. Maddison

|
| Scientific Name | Rhipsideigma lugubris |
|---|---|
| Specimen Condition | Dead Specimen |
| Life Cycle Stage | adult |
| View | dorsal |
| Size | 12.5mm head-body length |
| Copyright |
©
Thomas Hörnschemeyer

|
| Scientific Name | Rhipsideigma cretaceotincta |
|---|---|
| Specimen Condition | Dead Specimen |
| Life Cycle Stage | adult |
| View | dorsal |
| Size | 17.5mm head-body length |
| Copyright |
©
Thomas Hörnschemeyer

|
About This Page
Thomas Hörnschemeyer

University Göttingen, Institute for Zoology & Anthropology, Dept. Morphology & Systematics
Correspondence regarding this page should be directed to Thomas Hörnschemeyer at
thoerns@gwdg.de
Page copyright © 2011 Thomas Hörnschemeyer
 Page: Tree of Life
Rhipsideigma .
Authored by
Thomas Hörnschemeyer.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
Page: Tree of Life
Rhipsideigma .
Authored by
Thomas Hörnschemeyer.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
- First online 10 February 2006
- Content changed 23 July 2011
Citing this page:
Hörnschemeyer, Thomas. 2011. Rhipsideigma . Version 23 July 2011 (under construction). http://tolweb.org/Rhipsideigma/9029/2011.07.23 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/










 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site