Hemiptera
True bugs, cicadas, leafhoppers, aphids, etc.
David R. Maddison

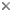
This tree diagram shows the relationships between several groups of organisms.
The root of the current tree connects the organisms featured in this tree to their containing group and the rest of the Tree of Life. The basal branching point in the tree represents the ancestor of the other groups in the tree. This ancestor diversified over time into several descendent subgroups, which are represented as internal nodes and terminal taxa to the right.

You can click on the root to travel down the Tree of Life all the way to the root of all Life, and you can click on the names of descendent subgroups to travel up the Tree of Life all the way to individual species.
For more information on ToL tree formatting, please see Interpreting the Tree or Classification. To learn more about phylogenetic trees, please visit our Phylogenetic Biology pages.
close boxIntroduction
Hemisys - half; pteron - wing; referring to the fact that many of its members have the basal half of the fore wings thicker than the distal half.Permian to Recent.
Characteristics
Derived characteristics:- mandiblulary and maxillary stylets coadapted, containing alimentary and salivary canals, enclosed in segmented labium
- holocentric chromosomes
References
Afifi, S. A. 1968. Morphology and taxonomy of the adult males of families, Pseudococcidae and Eriococcidae (Homoptera; Coccoidea). British Museum (Natural History), London: 210 pp.
Ahmad, I. and M. Moizuddin. 1990. A revision of Acanthosomatidae (Hemiptera: Pentatomomorpha: Pentatomoidea) from Indo-Pakistan area with a cladistic analysis of the genera. Oriental Insects 24(0): 267-304.
Andersen, N. M. 1982. The Semiaquatic Bugs (Hemiptera, Gerromorpha) Phylogeny, Adaptations, Biogeography and Classification. Entomonograph vol. 3, Klampanborg, Denmark.
Bourgoin, T. 1986. Imaginal morphology of the tentorium of Hemiptera, Fulgoromorpha. International Journal Of Insect Morphology And Embryology 15(4): 237-252.
Bourgoin, T. 1986. Morphological value of the maxillary plate in the Hemiptera: Phylogenetic remarks. Annales De La Societe Entomologique De France 22(4): 413-422.
Bourgoin, T. and B. C. Campbell. 2002. Inferring a phylogeny for Hemiptera: falling into the 'Autapomorphic Trap.' Denisia 4:67-82.
Campbell, B.C., J.D. Steffen-Campbell, and R.J. Gill. 1994. Evolutionary origin of whiteflies (Hemiptera: Sternorrhyncha: Aleyrodidae) inferred from 18S rDNA sequences. Insect Molecular Biology, 3: 73-88.
Campbell, B.C., J.D. Steffen-Campbell, J.T. Sorensen, and R.J. Gill. 1995. Paraphyly of Homoptera and Auchenorrhyncha inferred from 18S rDNA nucleotide sequences. Systematic Entomology, 20: 175-194.
Carver, M., G.F. Gross, and T.E. Woodward. 1991. Hemiptera. Pp. 429-509 in CSIRO, The Insects of Australia. Cornell University Press, Ithaca, New York.
Cobben, R. H. 1968,1978. Evolutionary trends in Heteroptera. Parts 1,2. Wageningen, Netherlands.
Dietrich, C. H. and L. L. Deitz. 1993. Superfamily Membracoidea (Homoptera: Auchenorrhyncha). II. Cladistic analysis and conclusions. Systematic Entomology, 18:297-311.
Dolling, W. R. 1991. The Hemiptera. Oxford University Press, London: 274 pp.
Drake, C. J. and Ruhoff, F. A. 1965. Lace bugs of the world: a catalogue (Hemiptera: Tingidae. Smithsonian Institution, Washington: 634 pp.
Evans, J.W. 1963, The phylogeny of the Homoptera. Ann.Rev.Ent 8:77-94.
Henry, T.J. & R.C.Froeschner, eds. 1988. Catalog of the Heteroptera, or True Bugs, of Canada and the Continental United States. E. J. Brill, Leiden.
Gullan, P. J. 2001. Why the taxon Homoptera does not exist. Entomologica 33:101-104.
Horvath, Geza. 1927. General catalogue of the Hemiptera. Smith College Pub, Northhampton, Mass: Vol 23.
Miller, N. C. E., 1956, Biology of the Heteroptera. Methuen, London
Parshley, H. M. 1925. A bibliography of North American Hemiptera-Heteroptera. Smith College Pub., Northhampton, Mass.: 252 pp.
Schaefer, C. W. (ed.) 1996. Studies on Hemipteran Phylogeny. Proceedings of Thomas Say Publications in Entomology, Entomological Society of America, Lanham, Maryland.
Schuh, R. T. 1979. Review of Cobben, Evolutionary trends in Heteroptera. Syst.Zool. 28:653-656.
Schuh, R. T. 1986, The influence of cladistics on heteropteran classification. Ann.Rev.Ent. 31: 67-94
Schuh, R. T. and P. Stys. 1991. Phylogenetic analysis of cimicomorphan family relationships (Heteroptera). Journal Of The New York Entomological Society 99(3): 298-350.
Schuh, R.T. and J.A. Slater. 1995. True Bugs of the World (Hemiptera: Heteroptera). Classification and Natural History. Cornell University Press, Ithaca, New York. xii + 336 pp.
Slater, J. A. & R. M. Baranowski, 1978. How to Know the True Bugs (Hemiptera - Heteroptera). Brown, Dubuque.
Sorensen, J.T., B.C. Campbell, R.J. Gill and J.D. Steffen-Campbell. 1995. Non-monophyly of Auchenorrhyncha ("Homoptera"), based upon 18S rDNA phylogeny: eco-evolutionary and cladistic implications within pre-heteropterodea Hemiptera (s.l.) and a proposal for new monophyletic suborders. Pan-Pacific Entomologist: 71 (1): 31-60.
Stys & Kerzhner, 1975. The rank and nomenclature of higher taxa in recent Heteroptera. Acta Ent. Bohemoslov. 72: 64-79.
Szelegiewicz, H. 1976. Autapomophous wing characters in the recent subgroups of Sternorrhyncha (Hemiptera) and their significance in the interpretation of the paleozoic members of the group. Foreign Sci. Pub. Dept., National Center for Scientific, Technical, and Economic Information: 61 pp.
Torre-Bueno, J. R. 1939. A synopsis of the Hemiptera-Heteroptera of America north of Mexico. Brooklin Entomological Society, Brooklin, New York: 122 pp.
Vasarhelyi, T. 1987. On the relationships of the eight aradid subfamilies (Heteroptera). Acta Zoologica Hungarica 33(1-2): 263-268.
von Dohlen, C.D. and N.A. Moran. 1995. Molecular phylogeny of the Homoptera: a paraphyletic taxon. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 41:211-223.
Wheeler, W.C., R.T. Schuh, and R. Bang. 1993. Cladistic relationships among higher groups of Heteroptera: congruence between morphological and molecular data sets. Ent. scand., 24:121-137.
Wootton, R. J. and C. R. Betts. 1986. Homology and function in the wings of Heteroptera. Systematic Entomology 11(3): 389-400.
Wygodzinsky, P. W. and K. Schmidt. 1991. Revision of the New World Enicocephalomorpha (Heteroptera). Bulletin Of The American Museum Of Natural History 0(200): 1-265.
Xie, Q., Y. Tian, L. Zheng, and W. Bu. 2008. 18S rRNA hyper-elongation and the phylogeny of Euhemiptera (Insecta: Hemiptera). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 47(2):463-471.
Zrzavy, J. 1992. Evolution of antennae and historical ecology of the hemipteran insects (Paraneoptera). Acta Entomologica Bohemoslovaca 89(2): 77-86.
Zrzavy, J. 1992. Morphogenesis of antennal exoskeleton in Heteroptera (Insecta): From phylogenetic to ontogenic pattern. Acta Entomologica Bohemoslovaca 89(3): 205-216.
Title Illustrations

| Scientific Name | Milviscutulus mangiferae |
|---|---|
| Acknowledgements | Courtesy of the Division of Plant Industry, Florida Department of Agriculture & Consumer Services |
| Specimen Condition | Live Specimen |
| Life Cycle Stage | Nymphs |
| Scientific Name | Cystosoma saundersii |
|---|---|
| Location | Brisbane, Australia |
| Comments | Bladder cicada |
| Specimen Condition | Live Specimen |
| Sex | Male |
| Life Cycle Stage | Adult |
| Size | 50mm |
| Copyright |
© Peter Chew

|
| Scientific Name | Melanocoryphus albomaculatus |
|---|---|
| Location | Germany |
| Specimen Condition | Live Specimen |
| Life Cycle Stage | Adult |
| Copyright |
© 2004 Frank Köhler

|
About This Page
David R. Maddison

Oregon State University
Correspondence regarding this page should be directed to David R. Maddison at
david.maddison@science.oregonstate.edu
Page copyright © 1995 David R. Maddison
 Page: Tree of Life
Hemiptera. True bugs, cicadas, leafhoppers, aphids, etc..
Authored by
David R. Maddison.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
Page: Tree of Life
Hemiptera. True bugs, cicadas, leafhoppers, aphids, etc..
Authored by
David R. Maddison.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
Citing this page:
Maddison, David R. 1995. Hemiptera. True bugs, cicadas, leafhoppers, aphids, etc.. Version 01 January 1995 (temporary). http://tolweb.org/Hemiptera/8239/1995.01.01 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/









 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site