Bolidophytes
Bolidomonas


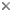
This tree diagram shows the relationships between several groups of organisms.
The root of the current tree connects the organisms featured in this tree to their containing group and the rest of the Tree of Life. The basal branching point in the tree represents the ancestor of the other groups in the tree. This ancestor diversified over time into several descendent subgroups, which are represented as internal nodes and terminal taxa to the right.

You can click on the root to travel down the Tree of Life all the way to the root of all Life, and you can click on the names of descendent subgroups to travel up the Tree of Life all the way to individual species.
For more information on ToL tree formatting, please see Interpreting the Tree or Classification. To learn more about phylogenetic trees, please visit our Phylogenetic Biology pages.
close boxIntroduction
The class Bolidophyceae includes a single genus Bolidomonas and two species (Bolidomonas pacifica and B. mediterranea) described from marine waters.
The Bolidophyceae was established by Guillou et al. (1999), as a new class of picoplankton isolated from both the equatorial Pacific and the Mediterranean Sea. One genus, Bolidomonas, and two species, Bolidomonas pacifica and B. mediterranea, have been described. Guillou et al. also proposed a subspecies of B. pacifica: B. pacifica var. eleuthra.
Bolidomonas pacifica swims differently than B. mediterranea, and their flagella are oriented differently with respect to one another (Fig. 1). B. pacifica swims in a consistently straight pattern, and the flagella are oriented at a 90° angle with respect to one another. In contrast, B. mediterranea demonstrates frequent changes in swimming direction, and flagella are oriented at a 180° angle with respect to one another.

Figure 1: The two flagella are oriented differently to one another in Bolidomonas mediterranea and B. pacifica. © J. Craig Bailey
Characteristics
- Unicellular, picoplanktonic golden-brown colored photosynthetic eukaryotes; flagellate and rapidly motile.
- Cells are naked, with no walls, and are spherical to ovoid in shape with cell diameters of ~1.2 µm.
- Two unequal, laterally inserted flagella are present. The long flagellum is ~4-7 µm in length, with mastigonemes (tubular hairs) and three terminal filaments; lateral filaments are absent. The short flagellum is ~0.9-2.2 µm in length, naked and acronematic.
- Single chloroplast with a distinct ring genophore and girdle lamellae; photosynthetic lamella composed of three adpressed thylakoids; eyespot unknown.
- Photosynthetic pigments are similar to those of diatoms and include chlorophylls a and c, fucoxanthin, diadinoxanthin, diatoxanthin, and beta carotene.
- Part of the picoplankton community, with cell diameter of ~1.2 µm.
- Individual cells possess a single mitochondrion with tubular cristae and a single Golgi apparatus which is located near the basal bodies.
- Reduced flagellar root system consisting only of two basal bodies; transitional helix absent; two transitional plates present, with lower plate thinner and more difficult to observe than upper plate.
- Thought to undergo unusual flagellar duplication, as the long flagellum may be incorporated by an invagination of the cell membrane and emerges at the opposite side of its normal insertion.
- Ploidy level of motile cels, sexual reproduction, and the existence of siliceous forms in the life cycle are as yet unknown.
- Described from the equatorial Pacific Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea; found in both mesotrophic and oligotrophic waters.
Relationship of Bolidophytes to other Stramenopiles
Phylogenetic analyses of nuclear 18S rRNA and plastid-encoded rbcL sequences indicate – with robust support – that Bolidomonas spp. are sister to the diatoms (Bacillariophyceae).
About This Page
Page copyright © 2010
 Page: Tree of Life
Bolidophytes. Bolidomonas.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
Page: Tree of Life
Bolidophytes. Bolidomonas.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
- First online 28 April 2010
- Content changed 28 April 2010
Citing this page:
Tree of Life Web Project. 2010. Bolidophytes. Bolidomonas. Version 28 April 2010 (under construction). http://tolweb.org/Bolidomonas/142186/2010.04.28 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/




 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site