Ancyromonas sigmoides
David J. PattersonIntroduction
Ancyromonas sigmoides is the most widely reported species in the genus, as well as being the type species. It has been reported from freshwaters, soil and marine habitats from around the world. Lee and Patterson (2000) give a recent account.
Synonyms:"Bodo cephaloporus"
Characteristics
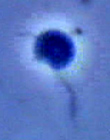
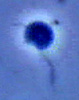
The cell outline is oval, and cells measure from 3 to 7 µm long; they are dorso-ventrally flattened. This species has a shallow groove ventrally near an antero-lateral margin of the cell. Cells may or may not have a thin stiff anterior flagellum emerging from an anterior depression. The anterior flagellum can be easily overlooked. The posterior flagellum is about 1.5 times the length of the cell and may have the same width along its length. The cell moves by gliding with the posterior flagellum trailing.
References
Lee, W. J. and Patterson, D. J. 2000. Heterotrophic flagellates (Protista) from marine sediments of Botany Bay, Australia. Journal of Natural History 34:483-562.
Kent, W. S. 1880-1882. Manual of the Infusoria. Three volumes, Bogue, London.
Title Illustrations

| Scientific Name | Ancyromonas sigmoides |
|---|---|
| Image Use |
 This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0. This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0.
|
| Copyright |
© 2000 David J. Patterson

|
| Scientific Name | Ancyromonas sigmoides |
|---|---|
| Comments | Phase contrast micrograph of living cell |
| Specimen Condition | Live Specimen |
| Image Use |
 This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0. This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0.
|
| Copyright |
© 2000 David J. Patterson

|
About This Page
David J. Patterson

Marine Biological Laboratory, Woods Hole, Massachusetts, USA
Page copyright © 2000 David J. Patterson
 Page: Tree of Life
Ancyromonas sigmoides .
Authored by
David J. Patterson.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
Page: Tree of Life
Ancyromonas sigmoides .
Authored by
David J. Patterson.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
- First online 04 October 2000
Citing this page:
Patterson, David J. 2000. Ancyromonas sigmoides . Version 04 October 2000. http://tolweb.org/Ancyromonas_sigmoides/2453/2000.10.04 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/






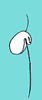

 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site